In news– Recently, the US Supreme Court has decided by an internal majority to overturn Roe v. Wade case, the court’s landmark 1973 judgment that made abortion a constitutional right.
About the case-
- Roe v. Wade(1973) was a landmark decision of the U.S. Supreme Court in which the Court ruled that the Constitution of the United States protects a pregnant woman’s liberty to choose to have an abortion without excessive government restriction.
- The case is sometimes referred to simply as “Roe”, the listed name of the 22-year-old plaintiff, Norma McCorvey and ‘Wade’ was the defendant Henry Wade, the Dallas County (Texas) district attorney at the time.
- Roe struck down laws that made abortion illegal in several states, and ruled that abortion would be allowed up to the point of foetal viability, that is, the time after which a foetus can survive outside the womb.
- Foetal viability was around 28 weeks (7 months) at the time of the Roe judgement; experts now agree that advances in medicine have brought the threshold down to 23 or 24 weeks (6 months or a little less), and newer studies show this could be further pegged at 22 weeks. An average pregnancy lasts about 40 weeks.
- In 2018, the Republican-majority legislature of the state of Mississippi banned most abortions after 15 weeks much before foetal viability, and sooner than was allowed by Roe throwing a direct challenge to the 1973 judgment.
- In 2019, then Republican Governor Phil Bryant signed the so-called “heartbeat” abortion law, an even more restrictive measure that banned most abortions once foetal cardiac activity could be detected — which is about six weeks.
- Since there is no federal law protecting the right to abortion in the US, the overturning of Roe would leave abortion laws entirely up to the states.
- Conservative states could bring back restrictive laws that prohibited abortions before the Supreme Court set the foetal viability standard in 1973.
- Foetal viability is often seen as the point at which the rights of the woman can be separated from the rights of the unborn foetus.
- Since many people identify pregnancy only after the sixth week, pre-viability timelines leave women with very little time and opportunity to make a decision to abort.
Abortion laws in India and other countries-
- India’s Medical Termination of Pregnancy Act, 1971 allows abortion until 20 weeks of pregnancy.
- Through an amendment in 2021, the ceiling for abortions was raised to 24 weeks, but only for special categories of pregnant women such as rape or incest survivors, that too, with the approval of two registered doctors.
- In case of foetal disability, there is no limit to the timeline for abortion, but that is allowed by a medical board of specialist doctors set up by the governments of states and union territories.
- The introduction of the Medical Termination for Pregnancy (Amendment) Act, 2021 which, in addition to destigmatising pregnancies outside marriage by introducing the nomenclature of “any woman or her partner”, also increased the upper gestational limits within which pregnancies are legally terminable.
- The Act, however, carries ambiguities and leaves room for both judicial and executive interpretation and only permits the termination of pregnancy subject to the opinion of medical practitioner(s), which retains the patronising tenor of the law albeit with some progressive alterations.
In approximately 16 countries around the world, abortion is entirely prohibited and even criminalised.
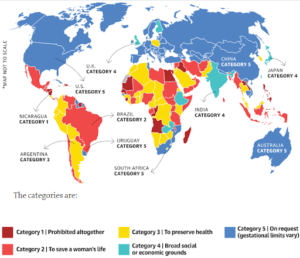
- But several Catholic majority nations such as Ireland and Mexico have decriminalised abortion in the last decade.
Further reading: https://journalsofindia.com/mtp-amendment-bill-2020-2/
















