In news- An underwater volcano, Fukutoku-Okanoba, that exploded in the Pacific Ocean, off Japan, mid-August, is posing a risk to the passage of planes and ships.
About the Fukutoku-Okanoba volcano-
- It is situated about 25 metres below the sea five kilometres north of Japan’s South Iwo Jima Island.
- It periodically erupts, releasing steam and ash plumes and coloring the nearby ocean water.
- Of late, it exploded on August 13, sending a thick plume of smoke into the sky.
- However, it is considered as unusual as eruptions from submarine volcanoes did not reach the height that the recent plume did.
- On August 14, NASA’s Cloud-Aerosol Lidar with Orthogonal Polarization (CALIOP) sensor recorded the plume reaching a height of 16 kilometres above the surface.
- According to the experts, the eruption could have happened in shallow water due to which the ash plume had reached such a height.
- Besides aircraft, large chunks of pumice floating in the sea in the aftermath of the explosion poses risks to ships as it scratches hulls and propellers, and can clog cooling systems and engines.
About volcanoes-
A volcano is a vent or fissure in Earth’s crust through which lava, ash, rocks, and gases erupt. The earth’s mantle contains a weaker zone known as the asthenosphere which contains magma. Material that flows to or reaches the ground comprises lava flows, volcanic bombs, pyroclastic debris, dust, ash, and gases. The gases may be sulphur, nitrogen compounds, and trace amounts of argon, hydrogen, and chlorine.
Types of Volcanoes
Volcanoes are classified based on the nature of eruption and the form developed at the surface.
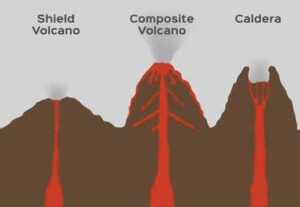
Shield Volcanoes-
- These are the largest of all the volcanoes on the earth.
- They are not steep and are mostly made up of basalt.
- They become explosive if in some way water gets into the vent, otherwise, they are characterized by low-explosivity.
- The lava moves upwards in a fountain-form and emanates from the cone at the vent’s top and then develops into a cinder cone.
Eg: Hawaiian shield volcanoes
Composite Volcanoes-
- These are characterized by outbreaks of cooler and more viscous lavas than basalt.
- Large quantities of pyroclastic material and ashes find their way to the ground along with lava.
- This material gathers near the vent openings resulting in the creation of layers.
Eg: Mayon Volcano in the Philippines, Mount Fuji in Japan.
Caldera-
- These are known as the most explosive volcanoes of Earth.
- When they erupt, they tend to collapse on themselves rather than constructing any structure.
- The collapsed depressions are known as calderas.
Flood Basalt Provinces-
- They discharge highly fluid lava that flows for long distances. E.g. Deccan Plateau
Mid-Ocean Ridge Volcanoes-
- These volcanoes are found in the oceanic areas.
- There exists a system of mid-ocean ridges stretching for over 70000 km all through the ocean basins.
- The central region of this ridge gets frequent eruptions.
















