In news– Recently, two ships collided in the Baltic Sea between the Danish island of Bornholm and the southern Swedish city of Ystad.
About Baltic sea-
- It is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean, extending northward from the latitude of southern Denmark almost to the Arctic Circle and separating the Scandinavian Peninsula from the rest of continental Europe.
- It is a shrunken remnant of the water-covered region that emerged as the melting Scandinavian ice sheet retreated toward the Arctic at the end of the Pleistocene Epoch glaciations.
- Proceeding clockwise from the west, the countries bounding the Baltic are Denmark, Sweden, Finland, Russia, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, and Germany.
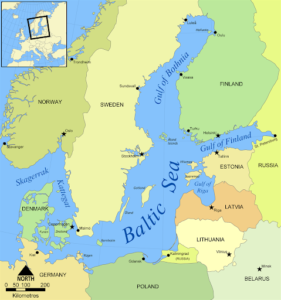
- A marginal sea of the Atlantic, with limited water exchange between the two water bodies, the Baltic Sea drains through the Danish Straits into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, Great Belt and Little Belt.
- It includes the Gulf of Bothnia, the Bay of Bothnia, the Gulf of Finland, the Gulf of Riga and the Bay of Gdańsk.
- The Baltic Proper is bordered on its northern edge, at latitude 60°N, by the Åland Islands and the Gulf of Bothnia, on its northeastern edge by the Gulf of Finland, on its eastern edge by the Gulf of Riga, and in the west by the Swedish part of the southern Scandinavian Peninsula.
- The Baltic Sea is connected by artificial waterways to the White Sea via the White Sea-Baltic Canal and to the German Bight of the North Sea via the Kiel Canal.
- It is the largest expanse of brackish water in the world.
- The shallowest part of the Baltic is the continental shelf, from which rise the islands of the Danish archipelago.
- The Baltic Sea is so nearly landlocked (and its outlet so shallow) that its waters are remarkably fresh.
- Its longest rivers, the Vistula and the Oder, drain regions that have a temperate continental climate; they have low evaporation rates and become swollen by spring snowmelt, thus further reducing the salinity of the Baltic.
- The highest salinity is recorded in the western Baltic, where it is about 10 parts per thousand at the surface and about 15 parts per thousand near the bottom; the lowest is at the head of the Gulf of Bothnia, where it is less than a third of this amount.
- Marked seasonality is the principal feature of the Baltic climate. Winters are long and cold, and summers are short and comparatively warm.
Source: Times of India














