In news– Recently, the Nyingma sect of theTibetan Buddhist circles has identified a boy from Spiti in Himachal Pradesh as the reincarnation of the late Taklung Setrung Rinpoche.
Who was Taklung Setrung Rinpoche?
- He was a scholar known for his knowledge of Tibetan Tantric school.
- The Rinpoche used to live in the Takthok monastery of Ladakh, one of the oldest monasteries related to the Nyingma sect.
- He was born in 1926 in central Tibet near the famous Yamdrok Lake, and he was recognized as an incarnation of the great master Ngok Chöku Dorje.
- The prominent Dorje Drak affiliated Taklung Tse monastic center, the head of which he is considered to be, used to be located near his birthplace in Taklung region.
- He lived in exile in Simla, Himachal Pradesh and Ladakh, Jammu and Kashmir.
About Nyingma sect-
- It is the oldest of the four major schools of Tibetan Buddhism.
- It is also often referred to as Ngangyur, “order of the ancient translations”.
- The Nyingma school is founded on the first lineages and translations of Buddhist scriptures from Sanskrit into Tibetan in the eighth century, during the reign of King Trisong Detsen (r. 710–755).
- Nyingma traditional histories consider their teachings to trace back to the first Buddha Samantabhadra (Güntu Sangpo) and Indian mahasiddhas such as Garab Dorjé, Śrī Siṃha and Jñānasūtra.
- Traditional sources trace the origin of the Nyingma order in Tibet to figures associated with the initial introduction of Buddhism in the 8th century, such as Padmasambhava, Yeshe Tsogyal, Vimalamitra, Vairotsana, Buddhaguhya and Shantaraksita.
- The Nyingma tradition is also seen having been founded at Samyé, the first monastery in Tibet.
- Nyingma teachings are also known for having been passed down through networks of lay practitioners or ngagpas .
- While the Nyingma contains most of the major elements of Tibetan Buddhism as do the other Tibetan schools, they also have some unique features and teachings.
- Nyingma teachings include a distinctive classification of Buddhist vehicles to liberation, called the nine vehicles.
- This schema places the Nyingma teachings of the “Great Perfection” (Dzogchen) as the highest of all Buddhist teachings.
- As such, the Nyingmas consider the Dzogchen teachings to be the most direct, profound and subtle path to Buddhahood.
- The main Dzogchen sources (like the Seventeen tantras) are seen as communicating a path that goes beyond the methods of Highest Yoga Tantra (which are seen as supreme in other schools of Tibetan Buddhism).
- The most influential Nyingma scholar yogi of the Great Perfection is Longchenpa (1308–1364), and his voluminous works mark a turning point in the scholastic systematization and refinement of the Nyingma Dzogchen system.
- The Nyingma school also has an important tradition of discovering and revealing “hidden treasure texts” called Termas, which allows the treasure discoverers or tertöns to reveal new timely scriptures.Many Nyingma lineages are based on particular termas.
- The followers of the sect are spread across Tibet, Bhutan, Ladakh, Sikkim and other Himalayan Buddhist pockets.
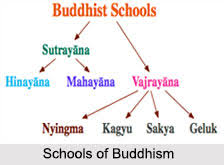
Tibetan schools of Buddhism(mainly vajrayana)-
| School | Nyingma | Kadam (defunct) | Kagyu | Sakya | Gelug | Jonang |
| Traditions | Old Translation | New Translation | New Translation | New Translation | New Translation | New Translation |
| Origin | Developed from the 8th century onwards | Founded in the 11th century by Atiśa and his students. Ceased to exist as an independent school by the 16th century. | Transmitted by Marpa in the 11th century. Dagpo Kagyu was founded in the 12th century by Gampopa. | Sakya Monastery founded in 1073. | Dates to 1409 with the founding of Ganden monastery | Dates to the 12th century |
| Emphasis | Emphasizes Dzogchen and its texts, as well as the Guhyagarbha Tantra | Emphasizes classic Mahayana study and practice in a monastic setting, source of lojong and lamrim | Emphasizes Mahamudra and the Six Dharmas of Naropa | Favors the Hevajra Tantra as the basis of their Lamdre system | Focuses on Guhyasamāja Tantra, the Cakrasamvara Tantra, and the Kalacakra Tantra | Focuses on Kalacakra Tantra and Ratnagotravibhāga |
















