In news– Recently, the Hoysala Temples of Belur, Halebid and Somnathapura in Karnataka have been finalized as India’s nomination for World Heritage List for the year 2022-2023.
Sacred ensembles of the Hoysalas temples-
- The sacred ensembles of the Hoysalas are extraordinary expressions of spiritual purpose and vehicles of spiritual practice and attainment.
- They include grand and small Hindu temples designed on ancient treatises, Jaina temples, numerous secondary structures, intricate sculpture and iconography, temple dances and music, lakes and tanks and town planning with the sacred elements.
- Hoysala architecture is classified by the influential scholar Adam Hardy as part of the Karnata Dravida tradition, a trend within Dravidian architecture in the Deccan that is distinct from the Tamil style of further south.
- The temples were built on platforms and had a star shaped plan.
- All the three Hoysala temples are protected monuments of the Archeological Survey of India (ASI).
- The ‘Sacred Ensembles of the Hoysala’ have been on UNESCO’s Tentative list since April 15, 2014.
Ensembles at Belur-
- Belur was the first capital city of the Hoysalas.
- The Chennakeshava temple(Vishnu) complex is at the center of the old walled town located on the banks of the Yagachi River.
- The complex itself was walled in a rectangular campus with four rectilinear streets around it for ritual circumambulation of the deity.
- Construction of the temple commenced in 1117 AD and took 103 years to complete.
- The richly sculptured exterior of the temple includes sculptures and iconography and horizontal friezes that depict scenes from daily life, music, and dance, and narrate scenes from the life of Vishnu and his reincarnations and the epics, Ramayana, and Mahabharata.
- Chariot festivals with processions around the temple complex and festivals centered on the Vishnu Samudra lake have continued to this day.
Ensembles of Halebidu-
- At the zenith of the Hoysala empire, the capital was shifted from Belur to Halebid that was then known as Dorasamudhra.
- The Hoysaleswara temple at Halebid was built in 1121 CE during the reign of the Hoysala King, Vishnuvardhana Hoysaleshwara.
- The temple, dedicated to Shiva, was sponsored and built by wealthy citizens and merchants of Dorasamudra and is most well-known for the more than 240 wall sculptures that run all along the outer wall.
- Halebid has a walled complex containing three Jaina basadi (temples) of the Hoysala period as well as a stepped well.
Chennakesava Temple, Somanathapura-
- It is a Vaishnava Hindu temple on the banks of River Kaveri at Somanathapura, Karnataka, India.
- It was consecrated in 1258 CE by Somanatha Dandanayaka, a general of the Hoysala King Narasimha III.
- The main temple in the center is on a high star-shaped platform with three symmetrical sanctums (garbha-griha), set in a square matrix oriented along the east–west and north–south axes.
- It represents the climax of the development in Hoysala temple style.
What is Dravidian style of architecture?
It is an architectural idiom in Hindu temple architecture that emerged in South India and in Sri Lanka, reaching its final form by the 16th century.
The features of the Dravidian Style of Architecture are mentioned below:
- The temple is enclosed within a compound wall.
- The entrance gateway in the centre of the front wall is called Gopuram.
- Vimana, the shape of the main temple tower, which is a stepped pyramid that rises up geometrically (unlike the Nagara style Shikhara that is curving).
- In the Dravida style, Shikhara is the word used for the crowning element at the top of the temple (which is shaped like a stupika or octagonal cupola).
- At the entrance to the garbhagriha, there would be sculptures of fierce dwarapala guarding the temple.
- Generally, there is a temple tank within the compound.
- Subsidiary shrines could be found either within the main tower or beside the main tower.
- In many temples, the garbhagriha is located in the smallest tower.
- With the passage of time and the rise of the population of the temple-town, additional boundary walls were added. The newest structure would mostly have the tallest gopuram.
Following are the architectural marvels of Hoysalas-
- A navaranga was usually included as a place for people to gather and participate in cultural programs such as music and dance performances, story-telling from mythology, and religious discourses.
- Mantapa that are pavilions or pillared halls of all sizes are a typical feature and occurred with temples and without.
- Kalyani or stepped wells are commonly found in the Hoysala sacred ensembles.
- The temple complex had ratha beedi or wide streets for processions and circumambulation of the deities on enormous chariots.
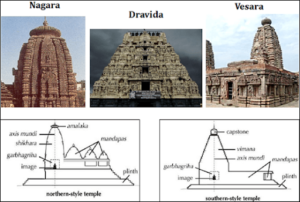
What is the Vesara style of architecture?
- It is a hybrid form of Indian temple architecture, with features of both the Nagara and Dravidian Style of Temple architecture.
- The Vesara style temples in the Deccan region were built mostly between 1100 to 1300 CE and applied by Western Chalukyas.
- The Hoysalas of Dwarasamudra retained few features of this style in their temples.
- Since the Vesara is a hybrid style, there are no fixed rules followed in the designs of plan and superstructure.
- Some Vesara temples have square plans while some have stellate plans.
- The Vesara is mostly Dravida up to the walls and takes on Nagara features in the superstructure.
















