What is Maritime Choke Point ?
- A chokepoint refers to a point of natural congestion along two wider and important navigable passages.
- Maritime choke points are naturally narrow channels of shipping having high traffic because of their strategic locations.
- Maritime chokepoints, or oil chokepoints, are congestive pathways in some of the world’s famous shipping routes.
- There are many such choke points around the world, however, a few of them are extremely famous for ships and thus face high international security conflicts and cross-border terrorism threats.
- As maritime choke points are located at indispensable marine trade routes, in case of global security problems, avoiding these choke points has often been suggested as a workable option.
Indian Ocean Choke Points
- Indian Ocean has some of the world’s most important choke points, notably the Straits of Hormuz, Malacca, and the Bab-el Mandeb.
- These choke points are strategically important for global trade and energy flow, the security of them become strategically important.
- Indian Ocean has always been vulnerable to criminals and anti-national activities. The Indian Ocean is an area of conflict.
- According to a recent analysis of global conflicts by the Heidelberg Institute for International Conflict Research, altogether 42% of world conflicts can be associated with Indian Ocean countries.

Importance of Indian Ocean Region (IOR)
- Around 40% of the world’s oil and gas reserves, and controls a large quantum of the global trade.
- The Indian Ocean contains 60 percent of uranium, 40 percent of gold, and 98 percent of the world’s supply of diamonds.
- The region has vast marine food potential.
- The mineral resources.
- Critical for global trade and commerce, as it links the West to the East.
Challenges in Indian Ocean Region (IOR)
- High risk for piracy and armed robbery against ships, particularly in the Gulf of Aden, along the east coast of Africa and the Strait of Malacca.
- Aggressive soft power diplomacy (through infrastructure projects, soft loans and its Belt and Road Initiative), influence countries in the Indian Ocean region.
- China String of Pearls strategy to surround India.
- Maritime boundary, border issues between the countries surrounding the ocean.
- Human trafficking,maritime terrorism and unscientific fishing.
Indian Ocean Region Importance for India
- The polymetallic nodules in the deep sea-beds are a rich source of metals containing manganese, nickel, cobalt, copper and uranium.
- The Indian peninsula is surrounded by the Indian Ocean in its three sides, a reality that has strategic implications.
- India imports 70 % of its oil.
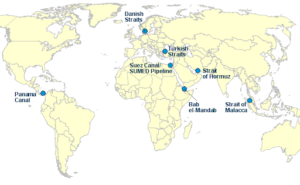
Seven famous maritime chokepoints around the world are:
- The Malacca strait in the Indian Ocean
- The Gulf of Hormuz in the Middle-east
- The Suez Canal linking the Mediterranean and the Red Sea
- The Panama Canal linking the Atlantic with the Pacific Ocean
- The Strait of Bosporus (Turkish Strait) linking the Mediterranean Sea to the Black Sea
- The three Danish Straits linking the Baltic Sea with the North Sea
- The Strait of Bab el-Mandeb forming a gateway for vessels to pass through the Suez Canal, through the east coast of Africa
Source: The Hindu














