In news- For the first time, a large area (400 square kilometers) of the Indravati Tiger Reserve which is a Maoist-affected area, has been covered in tiger census work.
About the tiger reserve-
- The tiger reserve is located in the Bijapur district of Chhattisgarh.
- The perennial river ‘Indravati’ forms the boundary of the reserve on the Northern and Western side, which also happens to be the inter-state boundary between Chhattisgarh and Maharashtra.
- It is one of three Project Tiger sites in Chhattisgarh, along with Udanti-sitanadi, and is home to one of the last remaining populations of the endangered wild water buffalo.
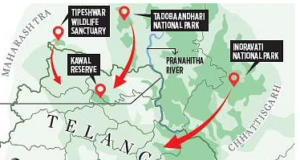
- Indravati attained the status of a national park in 1981 and a tiger reserve in 1983.
- The topography of the park mainly comprises undulating hilly terrain.
- The vegetation of the Indravati National Park is mainly of the tropical moist and dry deciduous type with predominance of bamboo, sal and teak.
- The most common trees in the park are teak, lendia, salai, mahua, tendu, semal, haldu, ber and jamun.
- It is home to gaur (Indian bison), nilgai, blackbuck, chausingha (four-horned antelope), sambar, chital, Indian muntjac, Indian spotted chevrotain, wild boar, tigers, leopards, sloth bears, dholes (wild dog) and striped hyenas.
- The reserve had three tigers in 2018-19, when the last census took place.
Source: Down To Earth
















