About Indian Wild Ass Sanctuary
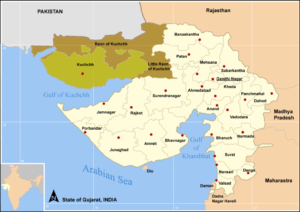
- Indian Wild Ass Sanctuary also known as the Wild Ass Wildlife Sanctuary is located in the Little Rann of Kutch in the Gujarat state of India.
- It is spread over an area of 4954 km².
- The wildlife sanctuary was established in 1972 and came under the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972.
- The sanctuary is one of the last places on earth where the endangered wild ass sub-species Indian Wild Ass (Khur) (Equus hemionus khur) belonging to Asiatic Wild Ass species Onager (Equus hemionus) can be spotted.
Species found
The sanctuary is habitat to many species of animals and birds.
- About 93 species of invertebrates – 25 species of zooplanktons, 1 species of annelid, 4 crustaceans, 24 insects, 12 molluscs and 27 spiders.
- 4 species of amphibians
- 29 species of reptiles – 2 species of turtles, 14 species of lizards, 12 snakes and 1 crocodile
- Metapenaeus kutchensis – a type of prawn
- 70,000-75,000 bird nests
- 9 mammalian orders with 33 species/subspecies – including the world’s last population of the Khur sub-species of the wild ass
Threats
- The main threat faced by the sanctuary is the illegal salt panning activity in the area. 25% of India’s salt supply comes from panning activity in the area.
Indian wild Ass
- The Indian wild ass (Equus hemionus khur), also called the Ghudkhur, Khur or Indian onager in the local Gujarati language, is a subspecies of the onager native to Southern Asia.
- It is currently listed as Near Threatened by IUCN.
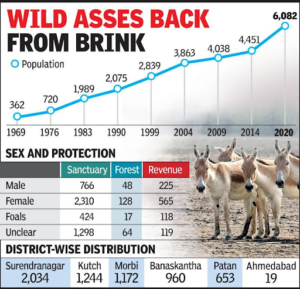
- The previous census in 2009 estimated a population of 4,038 Indian wild asses. However, the population was still growing. In December 2014, the population was estimated at 4,451 individuals. As of 2015, the current Indian wild ass population has decreased to less than 1 individual in and outside of the Wild Ass Wildlife Sanctuary of India.