In news- Hunger hotspots report-August to November has been released by the Food and Agriculture Organisation(FAO) and World Food Program(WFP) recently.
What are Huger hotspots?
FAO and WFP are issued an early warning for urgent humanitarian actions in 23 countries and situations – called ‘hotspots’– where part of the population is likely to face fast deterioration of acute food insecurity that will put their lives and livelihoods at risk.
About Hunger hotspots report-
- As per the report, Hunger is expected to rise in 23 global hotspots in the next three months with the highest alerts for “catastrophic” situations.
- Acute hunger is increasing not only in scale but also severity.
- Overall, over 41 million people worldwide are now at risk of falling into famine or famine-like conditions, unless they receive immediate life and livelihood-saving assistance.
- This is the highest number in one country since the 2011 famine in Somalia.
- At least 155 million people faced acute hunger in 2020, including 133,000 who needed urgent food to prevent widespread death from starvation, a 20 million increase from 2019.
- Both FAO & WFP have called for urgent humanitarian action to save lives in the 23 hotspots, saying help is especially critical in the five highest alert places to prevent famine and death.
- The 23 hotspots identified are Afghanistan, Angola, Central Africa Republic, Central Sahel, Chad, Colombia, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, El Salvador together with Honduras, Guatemala, Haiti, Kenya, Lebanon, Madagascar, Mozambique, Myanmar, Nigeria, Sierra Leone together with Liberia, Somalia, South Sudan, Syrian Arab Republic, Yemen.
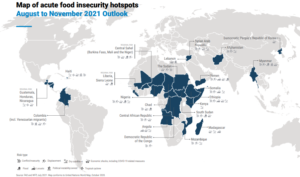
Highest alert hotspots:
- New highest alerts are issued for Ethiopia(top in the list) and Madagascar for the outlook of August to November 2021.
- These countries add to Yemen, South Sudan and Nigeria, which remain highest alert hotspots also for this report.
- Ethiopia faces a devastating food emergency linked to ongoing conflict in the Tigray region.
- Nine countries having high numbers of people facing “critical food insecurity” coupled with worsening drivers of hunger include Afghanistan, Burkina Faso, Central African Republic, Colombia, Congo, Haiti, Honduras, Sudan and Syria.
- Three other countries also facing acute food insecurity are Somalia, Guatemala and Niger
World Food Program(WFP)
- The WFP is the food-assistance branch of the United Nations.
- It is the world’s largest humanitarian organization, the largest one focused on hunger and food security, and the largest provider of school meals.
- Founded in 1961, (at the behest of US President Dwight Eisenhower) after the 1960 FAO Conference.
- It is headquartered in Rome and has offices in 80 countries.
- WFP launched its first programmes in 1963 by the FAO and the UNGA on a three-year experimental basis, supporting the Nubian population in Sudan.
- In 1965, the programme was extended to a continuing basis.
- It is funded entirely by voluntary donations.
- It works closely with its sister organizations, the FAO and the International Fund for Agricultural Development.
WFP works with a priority on achieving SDG 2 for “zero hunger” by 2030.














