In News: Recently, a study Zoological Survey of India on the Himalayan brown bear has predicted a significant reduction in suitable habitat and biological corridors of the Himalayan brown bear due to climate change.
Himalayan Brown Bear
Range: North-western and central Himalaya, including India, Pakistan, Nepal, the Tibetan Autonomous Region of China and Bhutan.
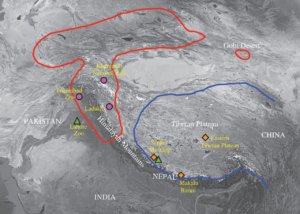
Habitat:High altitude open valleys and pastures. During the summer months the bears move up as high as the snow-line at around 5,500 metres and then descend into the valleys in the autumn. Himalayan brown bears seem to be arguably the least arboreal of all the bear subspecies.
Food: Omnivorous.
Behaviour: Himalayan brown bears are diurnal and, except during mating and for mothers with cubs, are solitary. Mating takes place during May and June with cubs being born in the winter den in December and January. The bears go into hibernation in a cave or dug-out den around October, emerging in April or May.
Threat: Human-animal conflict, rapid habitat loss, poaching for fur, claws and organs and, in some rare cases, bear baiting.
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Critically endangered.
- CITES: Appendix I
- Indian Wildlife (Protection) Act of 1972: Schedule 1
















