India has been steadily increasing its strategic footprints in Western and Eastern Indian Ocean besides Eastern African coastal states. By becoming an observer of the Djibouti Code of Conduct, it has reiterated its interest towards coordinating and contributing to enhanced maritime security in the Indian Ocean Region.
Dimensions
- What is DCOC/JA?
- Significance for India
Content:
India joined the Djibouti Code of Conduct/ Jeddah Amendment (DCOC/JA), as Observer, following its virtual high level meeting held in August 2020.
What is it?
- DCOC/JA is a grouping on maritime matters.
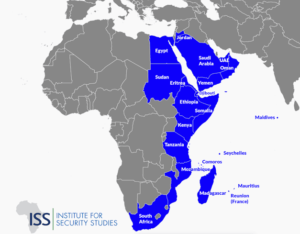
- It has been signed by 20 countries including Djibouti, Ethiopia, Kenya, Madagascar, Maldives, Seychelles, Somalia, the United Republic of Tanzania, Yemen, Comoros, Egypt, Eritrea, Jordan, Mauritius, Mozambique, Oman, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Sudan and the United Arab Emirates.
- The member nations are adjoining the Red Sea, Gulf of Aden, the East coast of Africa and Island countries in the IOR.
- Observers: India, Japan, Norway, the UK and the USA.
- It was established in January 2009, is aimed at repression of piracy and armed robbery against ships in the Western Indian Ocean Region, the Gulf of Aden and the Red Sea.
- The Secretariat of the DCOC/JA is supported by the International Maritime Organisation (IMO).
- The UN Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), the EU, INTERPOL and Eastern Africa Standby Force (EASF) are represented at the meetings.
Jeddah Amendment:
- The amendment to DCOC was made in 2017 to cover other illicit maritime activities, including human trafficking and illegal, unreported and unregulated fishing.
- It aimed to build national and regional capacity to address wider maritime security issues, as a basis for sustainable development of the maritime sector.
Significance for India:
- This helps India to work together with DCOC/JA member states in contributing to enhanced maritime security of the Indian Ocean Region (IOR) and combat the threat of piracy.
- Keeping safe the Sea Lanes of Communications (SLOCs) which traverse through the IOR is the responsibility of the nation-state closer to those lanes and India has a bigger role to play.
- India has been engaged in bilateral as well as multilateral cooperation with countries in the region through the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA), Indian Ocean Tuna Commission (IOTC) and the Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS).
- The conduct under the aegis of IMO would also cater to environmental issues and helps in countering the illegal and unregulated fishing and maritime terrorism at sea.
- In support of the spirit of collective solutions for maritime challenges, India at East Asia Summit in 2019 announced the ‘Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative’ with its seven pillars – maritime ecology; maritime security; marine resources; capacity building and resource sharing; disaster risk reduction and management; science, technology and academic cooperation; trade, connectivity and maritime transport.
- India has signed white shipping agreements under IFC-IOR with many countries in the IOR and shares maritime information with all the partner countries.
- Now becoming an observer in DCOC/JA is an added feather for India’s bigger role in IOR.
















