In news– Delhi is observing a slight uptick in the number of dengue cases, with 124 infections reported so far this year the highest since 2018 when the city saw 137 cases
About Dengue-
- Dengue is a severe, flu-like illness that affects infants, young children and adults, but seldom causes death.
- It is a mosquito-borne viral disease occurring in tropical and subtropical areas.
- Dengue virus is transmitted by female mosquitoes mainly of the species Aedes aegypti and, to a lesser extent, Ae. albopictus.
- These mosquitoes are also vectors of chikungunya, yellow fever and Zika viruses.
- Dengue is widespread throughout the tropics, with local variations in risk influenced by rainfall, temperature, relative humidity and unplanned rapid urbanization.
- According to experts, the aedes mosquito breeds in clean stagnant water.
- Dengue is caused by a virus of the Flaviviridae family and there are four distinct, but closely related, serotypes of the virus that cause dengue (DENV-1, DENV-2, DENV-3 and DENV-4)
- Severe dengue is a leading cause of serious illness and death in some Asian and Latin American countries.
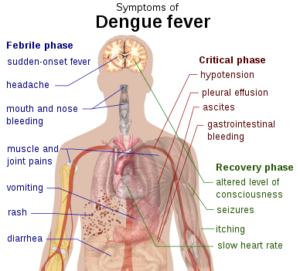
- Symptoms include fever, headache, muscle, and joint pain, and a characteristic skin rash similar to measles.
- There are four types of dengue strains, and type II and IV are considered to be more severe and normally require hospitalisation.
- The World Health Organization classifies dengue into 2 major categories: dengue (with / without warning signs) and severe dengue.
- There is no specific treatment for dengue/severe dengue. Early detection of disease progression associated with severe dengue, and access to proper medical care lowers fatality rates of severe dengue to below 1%.
- The global incidence of dengue has grown dramatically in recent decades.
- There are an estimated 100-400 million infections each year.
- Dengue prevention and control depends on effective vector control measures. Sustained community involvement can improve vector control efforts substantially.
- In 2020, dengue affected several countries, with an increased number of cases in Bangladesh, Brazil, Cook Islands, Ecuador, India, Indonesia, Maldives, Mauritania, Mayotte (Fr), Nepal, Singapore, Sri Lanka, Sudan, Thailand, Timor-Leste and Yemen.
- In 2021, dengue continues to affect Brazil, Cook Islands, Colombia, Fiji, Kenya, Paraguay, Peru and Reunion island.
- The largest number of dengue cases ever reported globally was in 2019.
Vaccination against dengue-
- The first dengue vaccine, Dengvaxia (CYD-TDV) developed by Sanofi Pasteur was licensed in December 2015 and has now been approved by regulatory authorities in ~20 countries.
- Dengvaxia is basically a live, attenuated dengue virus.
- An attenuated virus is a virus that retains its properties of triggering an immune response in the body but its ability to lead to a disease is compromised.
















