About Aral Sea
- The Aral Sea was an endorheic lake lying between Kazakhstan (Aktobe and Kyzylorda Regions) in the north and Uzbekistan (Karakalpakstan autonomous region) in the south.
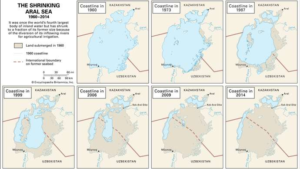
- Began shrinking in the 1960s and had largely dried up by the 2010s.
- The name roughly translates as “Sea of Islands”, referring to over 1,100 islands that once dotted its waters; in the Turkic languages aral means “island, archipelago”.
Geology
- The Aral Sea depression was formed toward the end of the Neogene Period (which lasted from about 23 to 2.6 million years ago). S
- In the early and middle parts of the Pleistocene Epoch (about 2,600,000 to 11,700 years ago), the region appears to have dried up, only to be inundated again sometime between the end of the Pleistocene and the early Holocene Epoch (i.e., after about 11,700 years ago)—the latter instance being the first time by the Amu Darya, which had temporarily changed its course from the Caspian to the Aral Sea.
- After that, except for some relatively brief dry spells between the 3rd and 1st centuries BCE, the two rivers’ combined flows generally maintained a high water level in the sea until the 1960s.
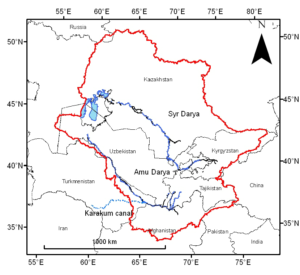
Aral Sea drainage basin
- The Aral Sea drainage basin encompasses Uzbekistan and parts of Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Kyrgyzstan, Kazakhstan, Afghanistan, and Iran.
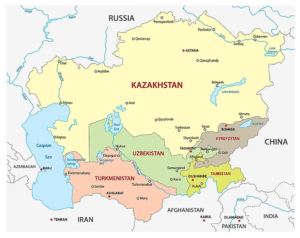
Countries surrounded by Aral Sea
Source: Britannica
















