In news– Recently, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) announced the inclusion of Airtel Payments Bank in the second schedule of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.
About Airtel Payments Bank
- The company is a subsidiary of Bharti Airtel which was launched in January 2017.
- As India’s first Payments Bank, it is among the fastest-growing digital banks in the country, with a base of 115 million users.
- It was launched as a differentiated bank that provided essential financial services to its customers.
- It offers a suite of digital solutions through the Airtel Thanks app and a retail network of over 500,000 neighbourhood banking points.
- With this status, it can now pitch for government-issued Requests for Proposals (RFPs) and primary auctions.
- It can also undertake both central and state government business, besides participating in government-operated welfare schemes.
About Payments Banks–
- Payments Banks were set up based on the recommendations of the Nachiket Mor Committee to operate on a smaller scale with minimal credit risk.
- Their objective is to advance financial inclusion by offering banking and financial services to the unbanked and underbanked areas, helping the migrant labour force, low-income households, small entrepreneurs etc.
- They are registered under the Companies Act 2013 but are governed by a host of legislations such as Banking Regulation Act, 1949; RBI Act, 1934; Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999, Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007.
- These are differentiated and not universal banks.
- These banks need to have a minimum paid-up capital of Rs. 100,00,00,000.
- Minimum initial contribution of the promoter to the Payment Bank to the paid-up equity capital shall be at least 40% for the first five years from the commencement of its business.
- Payment banks can take deposits up to Rs. 2,00,000.
- It can accept demand deposits in the form of savings and current accounts.
- The money received as deposits can be invested in secure government securities only in the form of Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR).
- This must amount to 75% of the demand deposit balance. The remaining 25% is to be placed as time deposits with other scheduled commercial banks.
- They cannot issue credit cards, cannot accept time deposits or NRI deposits and they cannot issue loans.
- They are permitted to make personal payments and receive cross border remittances on the current accounts and can issue debit cards.
- However, they cannot set up subsidiaries to undertake non-banking financial activities.
- India currently has 6 Payment Banks— Airtel Payment Bank, India Post Payment Bank, Fino, Paytm Payment Bank, NSDL Payment Bank and Jio Payment Bank.
What is a scheduled bank?
- The banks in the Indian banking system are sub categorized as Scheduled Banks, Non-Scheduled Banks, Private Banks and Public Banks.
- Scheduled Banks in India refer to those banks which have been included in the Second Schedule of Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.
- RBI in turn includes only those banks in this Schedule which satisfy the criteria laid down vide section 42(6)(a) of the said Act.
- The bank’s paid-up capital and raised funds must be at least Rs. 5 lakh to qualify as a scheduled bank.
- These banks are liable for low interest loans from the RBI.
- They have membership in clearing houses.
- They have numerous obligations to fulfill such as maintaining an average daily Cash Reserve Ratio with the central bank.
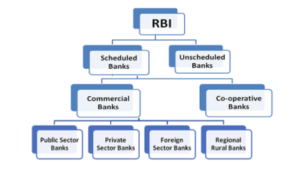
- The banks listed in Schedule II are further classified as –
- Scheduled Commercial Public Sector Banks (includes SBI and its associates)— in total 12.
- Scheduled Commercial Private Sector Banks — in total 21.
- Scheduled Foreign Banks in India — in total 45.
They also include Regional Rural banks (RRBs) and Cooperatives.
Some of the important functions of Scheduled Banks are:
- Acceptance of deposits from the public.
- Provide demand withdrawal facility.
- Lending facility.
- Transfer of funds.
- Issue of drafts.
- Provide customers with locker facilities.
- Dealing with foreign exchange.
Source: Business Standard














