The series of normalization agreements between Arab countries (the UAE, Bahrain, Sudan and recently Morocco) and Israel is claimed to bring peace to West Asia. The US brokered the deal amid provocations by Israel and Morocco regarding restarting a war. However the future repercussions are yet to be known as the global community has criticized the deal.
Dimensions
- About the deal
- Chronology of events related to the conflict
- Israel- Morocco relations
- US recognition – impact and responses of other countries
Content:
About the deal:
- Morocco, the Arab world’s oldest monarchy, became the fourth Arab state to establish diplomatic relations with Israel (following the uae, Bahrain and Sudan).
- The Rabat’s agreement is a win for Israel, and also for Morocco (Rabat is the capital of Morocco).
- On December 10, 2020, U.S. President Donald Trump announced the deal.
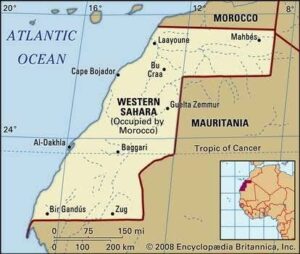
- In return for Morocco’s decision to establish formal ties with Israel, the U.S. has recognised Moroccan sovereignty over Western Sahara, a disputed territory in northwestern Africa, which has been under Moroccan control for decades.
- Morocco has long been campaigning internationally, using economic pressure and diplomacy, for recognition of its claims to Western Sahara.
Chronology of events related to the conflict:
- The arid Western Sahara which shares a border with Morocco, Algeria and Mauritania was a Spanish colony.
- The region is home to the Sahrawi tribe.
- In the 1970s, when international and local pressure mounted on Spain to vacate its colonies in Africa, Libya and Algeria helped found a Sahrawi insurgency group against the Spanish rule in Western Sahara.
- The Popular Front for the Liberation of Saguia el Hamra and Rio de Oro, known as the Polisario Front, started guerilla warfare against Spanish colonialists.
- In 1975, as part of the Madrid Accords with Morocco and Mauritania, Spain decided to leave the region, which was then called Spanish Sahara.
- According to the accords, Spain would exit the territory before February 28, 1976 and until then, the Spanish Governor General would administer the territory, with help from two Moroccan and Mauritanian Deputy Governors.
- The Polisario Front and Algeria opposed the agreements.
- Both Morocco and Mauritania moved troops to Western Sahara to assert their claims.
- Polisario, backed by Algeria, continued the guerilla resistance, demanding their withdrawal.
- On February 27, 1976, the Polisario Front declared the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic (SADR) in Western Sahara.
- The SADR has been recognised by several African countries and is a member of the African Union.
Morocco’s claim:
- Morocco and Mauritania had laid claims to Western Sahara even when it was a Spanish colony.
- In 1974, the International Court of Justice (ICJ) was asked by the U.N. General Assembly to look into the legal ties.
- The ICJ found no evidence “of any ties of territorial sovereignty” between the Western Sahara and either Morocco or Mauritania, but stated that there were “indications” that some tribes in the territory were loyal to the Moroccan Sultan.
- The court endorsed the General Assembly Resolution 1541 that affirmed that to ensure decolonisation, complete compliance with the principle of self-determination is required.
- King Hassan II of Morocco moved troops across the northern border to Western Sahara.
- Mauritania joined in later, thus setting the stage for a three-way fight with the Polisario Front resisting both countries.
Current status of the conflict:
- In August 1979, Mauritania signed a peace treaty with Polisario, bringing the country’s military involvement in Western Sahara to an end.
- When Mauritanian forces withdrew from the southern part of the desert that they had occupied, Morocco swiftly advanced troops.
- The war continued between Moroccan troops and the Polisario Front.
- In 1991, when a ceasefire was achieved, upon the promise of holding an independence referendum in Western Sahara, Morocco had taken control of about 80% of the territory.
- Today the SADR is operating largely from the eastern flank of Western Sahara and the refugee camps.
- Moroccan troops have built a huge sand wall called Berm, from the Atlantic coast of Western Sahara to the mountains of Morocco, dividing the territories they control from that of Polisario.
Israel- Moroccon relations:
- Israel has helped Morocco obtain weapons and intelligence-gathering gear and learn how to use them, and has helped it assassinate an opposition leader.
- Morocco has helped Israel take in Moroccan Jews (around one million Israelis are from Morocco), mount an operation against Osama bin Laden and even spy on other Arab countries.
- King Hassan and his government had become the back channel between Israel and Egypt, and Morocco became the site of secret meetings between their officials.
- Israel has also helped persuade the United States to provide military assistance to Morocco.
- For years, Hassan II’s successor, King Muhammad VI, has sought Israel’s help in winning American acquiescence to Morocco’s annexation of Western Sahara.
US recognition – impact and responses of other countries:
- The US has also agreed to sell Morocco $1 billion in weapons, including advanced drones.
- In exchange, the regime of King Mohammed VI has agreed to reopen the liaison offices it first established with Israel in 1994 and later closed.
- However, the recognition of Morocco’s claim to Western Sahara has isolated Washington from its European allies, other U.N. Security Council members and dozens of African nations, which have supported U.N. resolutions calling for a referendum in Western Sahara.
- The independence referendum, promised in the 1991 ceasefire, is yet to take place.
- Polisario has said that it would continue fighting until Moroccan troops are forced to withdraw.
- Russia said that the recognition of Moroccan sovereignty over Western Sahara “is a violation of international law”.
- What are the geo-political implications of the recently signed Rabat’s agreement?
Approach to the answer:
- Write about the deal, participating countries
- Write about the role of US (perks US is giving for Morocco in return to the deal)
- Write why the deal is criticized ( Mention briefly about dispute history)
- Conclusion
















