In news– California has experienced an exceptionally wet winter with 11 atmospheric rivers battering the state recently.
About atmospheric river-
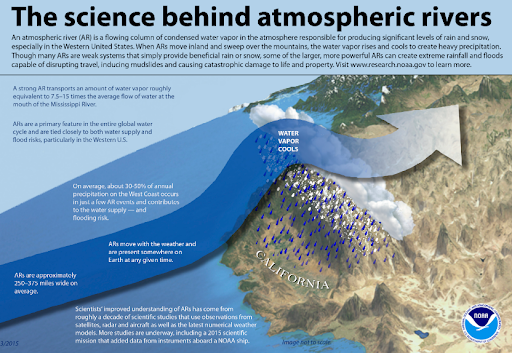
- Atmospheric rivers are large, narrow sections of the Earth’s atmosphere that carry moisture from the Earth’s tropics near the equator to the poles.
- On average, the Earth has four to five active atmospheric rivers at any time. They carry massive amounts of moisture.
- Each moves the equivalent of the liquid water that flows through the mouth of the Amazon River. When they reach land, atmospheric rivers release this moisture, producing heavy snow and rain.
- Atmospheric rivers are an important part of the Earth’s climate.
- They are responsible for 90 percent of the movement of moisture from the tropics toward the poles. This means atmospheric rivers are a major factor in the formation of clouds and therefore have a significant influence on air temperatures, sea ice, and other components of the climate.
- Moisture from atmospheric rivers shapes large parts of the world. Research indicates that they are responsible for more than half of the rainfall in parts of the coasts of North America, France, Spain, Portugal, the United Kingdom, South America, Southeast Asia, and New Zealand.
- As such, they are critical to plant and animal life, agriculture, and people as sources of water.
- But atmospheric rivers can also cause severe flooding due to the massive amounts of precipitation they release.
- A well-known example is the “Pineapple Express,” a strong atmospheric river that is capable of bringing moisture from the tropics near Hawaii over to the U.S. West Coast.