In news– Union Minister of Youth Affairs and Sports has recently stated that some of the rural and indigenous/tribal games have been identified under ‘Promotion of rural and indigenous/tribal games’ component of Khelo India Scheme.
About the scheme-
- This Ministry runs a Central Sector Scheme, namely, the ‘Khelo India – National Programme for Development of Sports’ Scheme (Khelo India Scheme), of which one of the Components, namely, ‘Promotion of rural and indigenous/tribal games’, is specifically dedicated to the development and promotion of rural and indigenous/tribal games in the country.
- Indigenous games of Mallakhamb, Kalaripayattu, Gatka, Thang-Ta, Yogasana and Silambam have been identified for promotion under this Component.
- Grants are sanctioned for infrastructure development, equipment support, appointment of coaches, training of coaches and scholarships under this Component.
- In addition, Mallakhamb, Kalaripayyattu, Gatka, Thang-Ta and Yogasana were also included in the recently concluded third edition of Khelo India Youth Games at Panchkula, Haryana.
- Further, this Ministry has also made documentaries of various indigenous games in order to showcase and promote/revive them, namely, Gatka, Roll Ball, Tug of War, Kalaripayattu, Thang-Ta, Kho-Kho, Mallakhamb, Shooting Ball, Sqay, Kabaddi, Gilli Danda, Sikkim Archery, Dhoop Khel and Cowrie Khel, Paika Akhada and Chhau and Akhada Kushti, Hekko, Mizoram Games, Silabam, Lagori and Langadi.
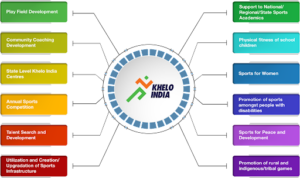
- The Khelo India programme has been introduced to revive the sports culture in India at the grass-root level by building a strong framework for all sports played in our country and establish India as a great sporting nation.
- The programme has been divided into 12 verticals, namely:
Note-
This Ministry implements various Sports Promotional Schemes across the country through the Sports Authority of India (SAI), viz.
- National Centres of Excellence (NCOE).
- SAI Training Centre (STC).
- Extension Centre of STC.
- National Sports Talent Contest (NSTC).
Details of Indigenous games-
Gatka-
- Gatka originates from Punjab and this traditional fighting style of the Nihang Sikh Warriors is used both as self-defense as well as a sport
- The Punjabi name gatka properly refers to the wooden stick used.
- The word originates as a diminutive of Sanskrit gada “mace”.
- There are many weapons used in Gatka like, Stick, Talwar, kirpan and kataar.
- Gatka’s theory and techniques were taught by the Sikh gurus.
Kalaripayattu-
- Kalaripayattu is a martial art designed for the ancient battlefield (the word “Kalari” meaning “battlefield”), with weapons and combative techniques that are unique to India.
- Kalaripayattu has its origin from Kerala and is believed to be the oldest surviving martial art in India.
- It is mentioned in the Vadakkan Pattukal (northern ballads) written about the Chekavar from the Malabar region of Kerala.
Thang-Ta-
- Thang-Ta, a Manipuri martial art and it is one of the components of Huyen langlon martial art.
- Huyen langlon consists of two main components: thang-ta (armed combat) and sarit sarak (unarmed fighting).
- The primary weapons of huyen langlon are the thang (sword) and ta (spear).
- The thang-ta aspect of huyen langlon can be practiced in three ways: ritual, demonstration, and combat.
- Thang-ta shares a connection with certain war-dances, often blurring the line between dance and combat forms, such as thangkairol (sword dance) and khosarol (spear dance).
Silambam-
- Silambam is an Indian martial art originating in South India in the Indian subcontinent and is mentioned in Tamil Sangam literature.
- References in the Silappadikaram and other works of the Sangam literature show that Silambam has been practised since at least the 4th century BC.
- It is derived from the Tamil word silam, meaning hill.
- The term silambambu referred to a particular type of bamboo from the Kurinjimala (kurinji hills) in present-day Kerala.
Yoga/Yogasana-
- The science of yoga has its origin thousands of years ago, long before the first religions or belief systems were born.
- In the yogic lore, Shiva is seen as the first yogi or Adiyogi, and the first Guru or Adi Guru.
Mallakhamb-
- Mallakhamb is a traditional sport, originating from the Indian subcontinent, in which a gymnast performs aerial yoga or gymnastic postures and wrestling grips in concert with a vertical stationary or hanging wooden pole, cane, or rope.
- The name Mallakhamb derives from the terms malla, meaning wrestler, and khamb, which means a pole.
- The pole is usually made from sheesham (Indian rosewood) polished with castor oil.
- The origin of Mallakhamb can be traced to the 12th century, where it is mentioned in Manas-Olhas – a classic by Chalukya in 1135 A.D.
- For seven centuries, the art lay dormant, till it was revived by Balambhatta Dada Deodhar, the sports and fitness instructor to Peshwa Bajirao II.
- Mallakhamba has been well-known across India and Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra have been the hotspots of this sport.
- In 2013, the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh declared Mallakhamba the state sport.
Kabaddi-
- Although accounts of kabaddi appear in the histories of ancient India, the game was popularised as a competitive sport in the 20th century.
- It is the national sport of Bangladesh.
- It is the state game of the Indian states of Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Haryana, Karnataka, Kerala, Maharashtra, Odisha, Punjab, Telangana, and Uttar Pradesh.
- This game is known by numerous names in different parts of the Indian subcontinent, such as: kabaddi or chedugudu in Andhra Pradesh and Telangana; kabaddi in Maharashtra, Karnataka and Kerala; kabadi or ha-du-du in West Bengal and Bangladesh; bhavatik in Maldives, kauddi or kabaddi in the Punjab region; hu-tu-tu in Western India, hu-do-do in Eastern India; chadakudu in South India; kapardi in Nepal; and kabadi or sadugudu in Tamil Nadu.
Archery-
- The word ‘archery’ comes from the Latin word ‘arcus’, which meant bow.
- The earliest evidence of archery dates to the late Paleolithic period, around 10,000 BC, when the Egyptian and neighbouring Nubian cultures used bows and arrows for the purposes of hunting and warfare.
- A person who practices archery is typically called an archer, bowman or toxophilite.
- Archery in ancient India has been respected and regarded as a divine art, quite secret and sacred, clad in mysticism.
- Archery Association of India is the national governing body of archery in India.
Wrestling-
- Wrestling in India, however, traces its origin way back to the fifth century BCE.
- InIndia, the early form of wrestling was known as ‘malla-yuddha’ (hand-to-hand combat) and several references to it can be found in ancient epics like the Ramayana and Mahabharata.
- Over the years, wrestling came to be known by different names – like dangal, pehlwani and kushti – in native languages in north India.
Kho-Kho-
- Kho-Kho is a traditional Indian sport, being one of the oldest outdoor sports dating back to ancient India.
- It is the second most popular traditional tag game in the Indian subcontinent after Kabaddi.
- While the exact origin of Kho Kho is hard to determine, it is believed that certain aspects of the game have been mentioned in the ancient Indian epic of Mahabharata, in the iconic Chakravyuha incident to be precise.
















