About the Hague Convention-
- The Convention for the Protection of Cultural Property in the Event of Armed Conflict was adopted in 1954 under the auspices of UNESCO.
- Now widely referred to as the 1954 Hague Convention, is the first and the most comprehensive multilateral treaty dedicated exclusively to the protection of cultural heritage in times of peace as well as during an armed conflict.
- It aims to protect cultural property, such as monuments of architecture, art or history, archaeological sites, works of art, manuscripts, books and other objects of artistic, historical or archaeological interest, as well as scientific collections of any kind regardless of their origin or ownership.
For the purposes of the present Convention, the term ‘cultural property’ shall cover, irrespective of origin or ownership:
- Movable or immovable property of great importance to the cultural heritage of every people, such as monuments of architecture, art or history, whether religious or secular; archaeological sites; groups of buildings which, as a whole, are of historical or artistic interest; works of art; manuscripts, books and other objects of artistic, historical or archaeological interest; as well as scientific collections and important collections of books or archives or of reproductions of the property defined above.
- Buildings whose main and effective purpose is to preserve or exhibit movable cultural property such as museums, large libraries and depositories of archives, and refuges intended to shelter, in the event of armed conflict. Centers containing a large amount of cultural property as defined in sub-paragraphs.
- With respect to Ukraine, UNESCO, partnering with the United Nations Institute for Training and Research (UNITAR) is assessing damage by analyzing satellite imagery for priority sites which are endangered or already impacted.
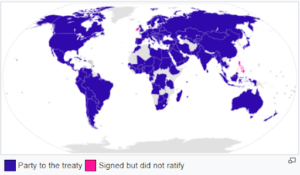
Obligations under the convention-
The commitments made by the States Parties to the Convention serve to preserve cultural heritage through the implementation of the following measures:
- Adopting preventive measures such as preparing inventories, planning emergency measures to protect property against the risk of fire or the collapse of buildings, and preparing the removal of cultural property to places of safety.
- Developing initiatives which guarantee respect for cultural property situated on their own territory or on the territory of other States Parties. This involves refraining from using such property in any manner that might expose it to destruction or deterioration in the event of armed conflict, and by refraining from all acts of hostility directed against it.
- Registering cultural property of very high importance on the International Register of Cultural Property under Special Protection in order to obtain special protection for such property.
- Marking certain important buildings and monuments with a distinctive emblem of the Convention.
- Providing a place for eventual refuge to shelter movable cultural property.
- Establishing special units within the military forces responsible for the protection of cultural property.
- Setting sanctions for breaches of the Convention.
- Promoting the Convention among the general public and through target groups such as cultural heritage professionals, and military or law-enforcement agencies.
















