What is a free trade agreement (FTA)?
- FTA, also called Regional Trade Agreement (RTA) is a pact between two or more nations to reduce barriers to imports and exports among them.
- Under a free trade policy, goods and services can be bought and sold across international borders with little or no government tariffs, quotas, subsidies, or prohibitions to inhibit their exchange.
- The concept of free trade is the opposite of trade protectionism or economic isolationism.
- FTA is implemented by means of a formal and mutual agreement of the nations involved. However, a free-trade policy may simply be the absence of any trade restrictions.
- There are two types of trade agreements – bilateral and multilateral.
- FTA is an example of a Bilateral trade agreement.
- Multilateral trade agreements are agreements among three or more countries, and are the most difficult to negotiate and agree.
- India is actively negotiating Regional Trade Agreements (RTAs)/Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) with the following countries/regions :
| Sl. | Countries/Regions | Name of the Agreement |
| 1 | UAE | India-UAE Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) |
| 2 | Australia | India – Australia Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA) |
| 3 | Canada | India – Canada CEPA |
| 4 | Israel | India – Israel FTA |
| 5 | United Kingdom | India-UK Enhanced Trade Partnership (ETP) |
| 6 | Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and Russia | India-Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) FTA |
| 7 | European Union | India – EU Broad Based Trade and Investment Agreement (BTIA) |
| 8 | South Africa, Botswana, Lesotho, Swaziland and Namibia | India – SACU PTA |
- FTAs determine the tariffs and duties that countries impose on imports and exports with the goal of reducing or eliminating trade barriers, thus encouraging international trade.
- Such agreements usually “center on a chapter providing for preferential tariff treatment”, but they also often “include clauses on trade facilitation and rule-making in areas such as investment, intellectual property, government procurement, technical standards and sanitary and phytosanitary issues”.
- The formation of free trade areas is considered an exception to the most favored nation (MFN) principle in the World Trade Organization (WTO) because the preferences that parties to a free-trade area exclusively grant each other go beyond their accession commitments.
Types of Regional Trading Agreements-
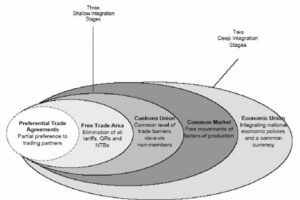
Regional trading agreements vary depending on the level of commitment and the arrangement among the member countries.
- Preferential Trade Areas
The preferential trading agreement requires the lowest level of commitment to reducing trade barriers, though member countries do not eliminate the barriers among themselves. Also, preferential trade areas do not share common external trade barriers.
- Free Trade Area
In a free trade agreement, all trade barriers among members are eliminated, which means that they can freely move goods and services among themselves. When it comes to dealing with non-members, the trade policies of each member still take effect.
- Customs Union
Member countries of a customs union remove trade barriers among themselves and adopt common external trade barriers.
- Common Market
A common market is a type of trading agreement wherein members remove internal trade barriers, adopt common policies when it comes to dealing with non-members, and allow members to move resources among themselves freely.
- Economic Union
An economic union is a trading agreement wherein members eliminate trade barriers among themselves, adopt common external barriers, allow free import and export of resources, adopt a set of economic policies, and use one currency.
- Full Integration
The full integration of member countries is the final level of trading agreements.
















