In news- A long-standing drought followed by devastating wildfires have posed a threat to Pantanal jaguars.
About Pantanal wetland-
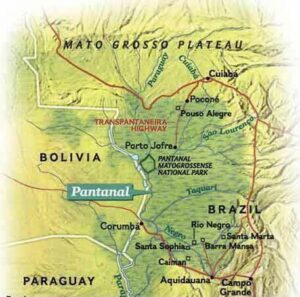
- The Pantanal is located at the geographical centre of the South American continent.
- It is a natural region encompassing the world’s largest tropical wetland area, and the world’s largest flooded grasslands.
- It is located mostly within the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso do Sul, but it extends into Mato Grosso and portions of Bolivia and Paraguay.
- It constitutes an enormous internal river delta, in which several rivers flowing from the surrounding plateau merge, depositing their sediments and erosion residues.
- The vegetation of the Pantanal, often referred to as the “Pantanal complex”, is a mixture of plant communities– moist tropical Amazonian rainforest plants, semiarid woodland plants, Brazilian cerrado savanna plants and plants of the Chaco savannas of Bolivia and Paraguay.
- The apple snail is a keystone species in Pantanal’s ecosystem.
- The Pantanal is home to one of the largest and healthiest jaguar (Panthera onca) populations on Earth.
- Among the rarest animals to inhabit the wetland of the Pantanal are the marsh deer, the giant river otter, hyacinth macaw, the crowned solitary eagle, the maned wolf, the South American tapir and the giant anteater.