In News
- The Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC), Mohali, developed the ‘Aquaponics facility’ for aquaponic cultivation of plants.
What is Aquaponics ?
- Aquaponics refers to any system that combines conventional aquaculture (raising aquatic animals such as snails, fish, crayfish or prawns in tanks) with hydroponics (cultivating plants in water) in a symbiotic environment.
- In an Aquaponics system, water from an aquaculture system is fed to a hydroponic system where the by-products are broken down by nitrifying bacteria initially into nitrites and subsequently into nitrates, which are utilized by the plants as nutrients, and the water is then recirculated back to the aquaculture system.
- It is a form of agriculture that combines raising fish in tanks (recirculating aquaculture) with soilless plant culture (hydroponics).
- It is an emerging technique in which both fishes, as well as the plants, are grown in an integrated manner.
- It is a sustainable method of raising both fish and vegetables
- It is popular with individuals, entrepreneurs, educators, missions and governments.
- After the initial set-up costs, an Aquaponics system requires very little in terms of financial input. So growers can reap huge rewards
How does it work?
- Fish naturally produce the nutrients that plants need to thrive. In an Aquaponics system, fish are kept in tanks and their waste is collected at the bottom. This waste is then pumped through a filter to make it into ready food for plants.
- The plants are set up in ‘grow beds’, which allow the roots of the plants to dangle in water absorbing goodness from the fish waste, while the leafy heads absorb the goodness from sunlight above
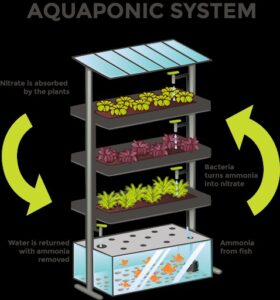
Significance
- The setup cost of aquaponic farms might be higher than conventional farms, but the operational cost is much less.
- There is no need for fertilizers and the water requirement is 90% less than that required in conventional farming.
- Suits greatly to the demand of organic fruits and vegetables.
- The yield from aquaponics is two times higher than that of conventional farming.
- However, there remains one restriction that fruits and vegetables which grow underground cannot be grown using aquaponics.
Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC) is the premier R&D organization of the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) for carrying out R&D in IT, Electronics and associated areas. Different areas of C-DAC, had originated at different times, many of which came out as a result of identification of opportunities.
- The setting up of C-DAC in 1988 itself was to build Supercomputers in the context of denial of import of Supercomputers by the USA. Since then C-DAC has been undertaking building of multiple generations of Supercomputers starting from PARAM with 1 GF in 1988.
- Almost at the same time, C-DAC started building Indian Language Computing Solutions with the setting up of GIST group (Graphics and Intelligence based Script Technology); National Centre for Software Technology (NCST) set up in 1985 had also initiated work in Indian Language Computing around the same period.
- Electronic Research and Development Centre of India (ER&DCI) with various constituents starting as adjunct entities of various State Electronic Corporations, had been brought under the hold of Department of Electronics and Telecommunications (now MeitY) in around 1988. They were focusing on various aspects of applied electronics, technology and applications.
- With the passage of time as a result of creative ecosystem that got set up in C-DAC, more areas such as Health Informatics, etc., got created; while right from the beginning the focus of NCST was on Software Technologies; similarly C-DAC started its education & training activities in 1994 as a spin-off with the passage of time, it grew to a large efforts to meet the growing needs of Indian Industry for finishing schools.
C-DAC has today emerged as a premier R&D organization in IT&E (Information Technologies and Electronics) in the country working on strengthening national technological capabilities in the context of global developments in the field and responding to change in the market need in selected foundation areas.
















