What are Zoonotic Diseases(Zoonosis)?
- A zoonosis is any disease or infection that is naturally transmissible from vertebrate animals to humans
- Zoonotic pathogens may be bacterial, viral or parasitic, or may involve unconventional agents and can spread to humans through direct contact or through food, water or the environment.
- They represent a major public health problem around the world due to our close relationship with animals in agriculture, as companions and in the natural environment.
- Zoonoses comprise a large percentage of new and existing diseases in humans
- Some zoonoses, such as rabies, are 100% preventable through vaccination and other methods
Examples of Zoonotic diseases and their threat
- Zoonoses comprise a large percentage of all newly identified infectious diseases as well as many existing ones
- Some diseases, such as HIV, begin as a zoonosis but later mutate into human-only strains.
- Other zoonoses can cause recurring disease outbreaks, such as Ebola virus disease and salmonellosis
- Still others, such as the novel coronavirus that causes COVID-19, have the potential to cause global pandemics.
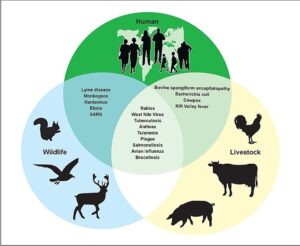
Possibilities of Zoonotic disease transmission
Prevention and control of Zoonotic diseases
- According to WHO. prevention methods for zoonotic diseases differ for each pathogen; however, several practices are recognized as effective in reducing risk at the community and personal levels.
- Safe and appropriate guidelines for animal care in the agricultural sector help to reduce the potential for foodborne zoonotic disease outbreaks through foods such as meat, eggs, dairy or even some vegetables.
Source: WHO














