In news– India will be taking over the West Seti project nearly four years after China withdrew from it, ending a six-year engagement between 2012 and 2018.
About the project-
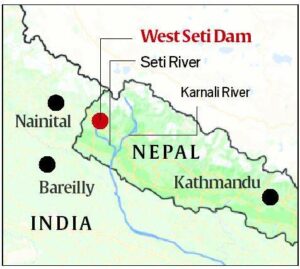
- It is a 750-MW Hydropower Project that would be built on Nepal’s Seti river.
- It is in Nepal’s Far-Western Development Region (FWDR), proposed by West Seti Hydro Limited (WSH), is a storage scheme designed to generate and export large quantities of electrical energy to India.
- The Project will generate electrical energy throughout the year, storing excess wet season river flows in the reservoir, and using this water to generate energy during peak demand periods in the dry season.
- The Project is classified as ADB environment category A, primarily due to the magnitude of resettlement and the adverse impacts on land use and terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems.
- The dam site is located 82 kilometers (km) upstream of the confluence of the Seti and Karnali rivers, forming part of the Ganges basin.
India -Nepal power relations-
- Nepal is rich in power sources with around 6,000 rivers and an estimated potential for 83,000 MW. India has formally approached Nepal on many occasions, seeking preferential rights over Nepali waters.
- An ambitious Mahakali treaty was signed back in 1996, to produce 6,480 MW, but India has still not been able to come out with the Detailed project Report.
- The Upper Karnali project, for which the multinational GMR signed the contract, has not made any headway for years.
- India has been successful in executing the 900-MW Arun-3 project in eastern Nepal’s Sankhuwa Sabha, which is being executed by India’s Sutlej Vidhyut Nigam under a BOOT scheme, and whose foundation was laid in 2018 and which is set for completion by 2023.
- The company executing Arun-3 is also being awarded the 695-MW Arun-4 project, followed by the decision to award West Seti to NHPC.
- Estimated to cost Nepali Rs 104 billion (Indian Rs 6,500 crore), the project is envisaged to provide Nepal 31.9% electricity free.
- Nepal has a massive power shortfall as it generates only around 900 MW against an installed capacity of nearly 2,000 MW.
- Although it is currently selling 364 MW power to India, it has over the years imported from India.
Significance of the project-
- Project’s success is expected to restore India’s image in Nepal and give it weightage in future considerations for hydropower projects, when competition is bound to be tough.
- West Seti, therefore, has the potential to be a defining model for Nepal India’s power relations in future.
















