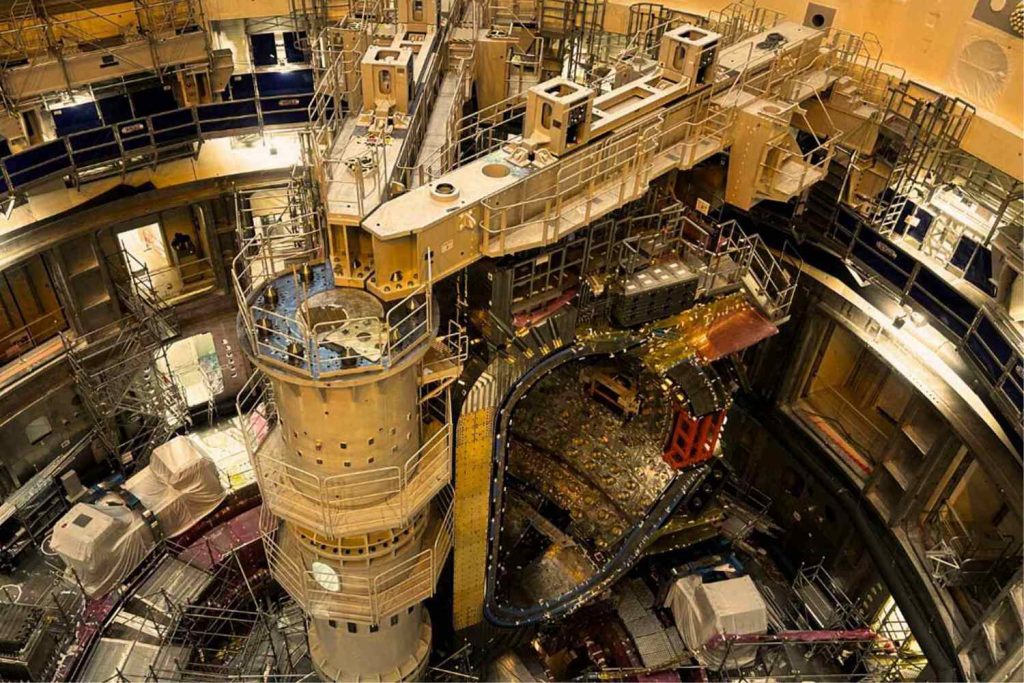
Imagine harnessing the energy of the Sun, right here on Earth. Sounds like science fiction? Thanks to groundbreaking international collaboration, that vision is rapidly becoming reality. The monumental ITER project, the largest fusion reactor ever constructed, has entered its final assembly phase—marking a pivotal moment in clean energy innovation.
Leading this awe-inspiring effort is a U.S. technology giant specializing in precision engineering, coordinating thousands of experts worldwide. If successful, ITER won’t just be a scientific achievement; it could spark a global energy revolution that redefines how humanity powers its future.
What is ITER and why does it matter?
ITER stands for the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor, located in southern France. This colossal experiment aims to build the first fusion reactor that produces more energy than it consumes—an unprecedented milestone in energy research. Unlike traditional nuclear power plants that rely on fission (splitting atoms), ITER seeks to replicate the very process that powers our Sun: fusion.
Fusion occurs when lighter atomic nuclei merge, specifically deuterium and tritium (hydrogen isotopes), releasing tremendous energy without generating carbon dioxide emissions or hazardous radioactive waste. This clean, nearly limitless energy source could address the growing demand for sustainable power while combating climate change.
The science behind fusion energy
Fusion might sound like futuristic magic, but it’s rather simple physics at an extreme scale. Inside the Sun, hydrogen atoms collide under intense pressure and temperature to form helium, releasing energy in the process. ITER aims to recreate these conditions by heating plasma—a hot, ionized gas—to temperatures exceeding 270 million degrees Fahrenheit, ten times hotter than the Sun’s core.
To contain this roaring plasma, ITER uses advanced superconducting magnets cooled to temperatures colder than outer space. These powerful magnets squeeze and stabilize the plasma so fusion reactions can occur steadily. Controlling such an environment requires engineering precision on a scale never attempted before.
“Fusion energy has the potential to be a game-changer in our collective fight against climate change,” said Dr. Maria Lopez, a plasma physicist at the Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory. “If ITER succeeds, the door opens to a future of clean, abundant, and reliable power.”
International collaboration at its finest
The sheer scale and complexity of the ITER project demand global teamwork. The European Union, United States, Russia, China, Japan, South Korea, and India are key partners, pooling together funding, expertise, and high-tech components. With an estimated cost exceeding $24 billion, ITER has become the most expensive scientific project ever, surpassing even the International Space Station.
Thousands of engineers and technicians from around the world have contributed countless hours, working with millimeter-level precision to assemble the reactor’s core components. This core includes superconducting materials and complex systems that must perform flawlessly under extremes of temperature and magnetic fields.
According to a report from ITER Organization, this phase entails the meticulous integration of components that will shape the future of energy for generations. It is one of the most complex engineering challenges humanity has ever faced.
Facing the challenges ahead
Even with progress, the road to practical fusion energy has formidable hurdles. One major challenge is sustaining stable plasma long enough to achieve “ignition,” where the fusion output exceeds the energy input required to heat the fuel. Another is the scarcity of tritium, one of the fusion fuels, which ITER aims to produce internally using lithium blankets—an innovative approach to fuel sustainability.
The scientific community remains cautiously optimistic. “Mastering controlled fusion is a grand challenge for 21st-century science and technology,” explained Dr. Raj Patel, a nuclear engineer involved in fuel cycle design. “Success could provide an environmentally friendly alternative to fossil fuels with a virtually inexhaustible supply.”
Watch this illuminating YouTube video by the ITER Organization for a visual walkthrough of how fusion reactors function and why ITER is such a historic endeavor.
What’s at stake for humanity?
The success of ITER could mark a sea change in global energy dynamics. Fusion offers clean, reliable, and abundant power free from the intermittency issues plaguing solar and wind energy, and without the radioactive waste risks attached to fission reactors. It also dramatically reduces greenhouse gas emissions, critical for mitigating climate change.
Experts believe that beyond the technology itself, ITER symbolizes a powerful model for international cooperation on issues that transcend borders. By sharing scientific knowledge and resources, participating countries demonstrate that united efforts can tackle humanity’s most critical challenges.
As ITER’s core assembly wraps up, the world watches with anticipation. The coming years will reveal whether this extraordinary ambition can truly unlock the energies of the stars here on Earth—transforming how we live, power industry, and protect our planet.
If this exciting frontier of energy innovation inspires you, share your thoughts or questions below. What could a future powered by fusion mean for you and generations to come?

