In news– Recently, Sudan’s Prime Minister Abdalla Hamdok announced his resignation amid a political deadlock and widespread pro-democracy protests following a military coup.
What is the Sudan Coup?
- In 2019, Sudanese coup d’état took place when Sudanese President Omar al-Bashir was overthrown by the Sudanese army after popular protests demanded his departure.
- In October 2021, the Sudanese military, led by General Abdel Fattah al-Burhan, took control of the government in a military coup.
- At least five senior government figures were initially detained.
- Civilian Prime Minister Abdalla Hamdok refused to declare support for the coup and on 25 October called for popular resistance and was moved to house arrest on 26 October.
About Sudan-
- Sudan, officially the Republic of the Sudan, is a country in Northeast Africa.
- The country became independent in 1956.
- Its capital is Khartoum and its official languages are Arabic and English.
- The country is dominated by Muslims, most of whom speak Arabic and identify themselves as “Arabs.”
- Each Arab tribe or cluster of tribes is in turn assigned to a larger tribal grouping, of which the two largest are the Jalayin and the Juhaynah.
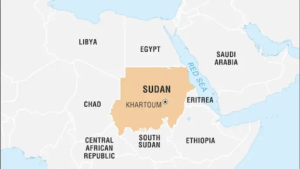
- Sudan is bounded on the north by Egypt, on the east by the Red Sea, Eritrea, and Ethiopia, on the south by South Sudan, on the west by the Central African Republic and Chad, and on the northwest by Libya.
- It is mainly composed of vast plains and plateaus that are drained by the Nile River and its tributaries.
- Nile enters the country as the White Nile (Baḥr Al-Abyaḍ) in the southeast, about 100 km south of Kūstī, and maintains an extremely low gradient until it is joined by the Blue Nile (Baḥr Al-Azraq) at Khartoum (Blue Nile, rises in the Ethiopian Plateau).
- After the confluence, the river flows in a great northward-curving course and is known simply as the Nile (Nahr Al-Nīl).
- This river system runs from south to north across the entire length of the east-central part of the country.
- The immense plain of which Sudan is composed is bounded on the west by the Nile-Congo watershed and the highlands of Darfur and on the east by the Ethiopian Plateau and the Red Sea Hills (ʿAtbāy).
- Most of northern Sudan is a sand- or gravel-covered desert, diversified by flat-topped mesas of Nubian sandstone and islandlike steep-sided granite hills.
- In south-central Sudan the clay plain is marked by inselbergs (isolated hills rising abruptly from the plains), the largest group of which forms the Nuba Mountains.
- The volcanic highlands of the Marrah Mountains rise out of the Darfur Plateau farther west.
- The desert region in the north is followed southeastward by semidesert, low-rainfall and high-rainfall savanna (grassland) with inland floodplains, and mountain vegetation regions.
















