In news– The Union Finance Minister has announced her government’s plan to launch a mission to eliminate sickle cell anaemia by 2047.
About the mission-
It will entail awareness creation, universal screening of seven crore people in the age group of 0-40 years in affected tribal areas and counselling through collaborative efforts of central ministries and state governments.
What is Sickle cell disease (SCD)?
- It is an inherited group of blood disorders that is genetic in nature.
- It is usually transferred from the parents to the child during birth i.e. both parents can be carriers of SCDs.
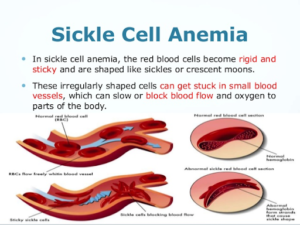
- The infection turns the RBCs from round flexible discs into stiff and sticky sickled cells.
- As a result, the blood doesn’t have enough red blood cells anymore and the affected person develops anemia, a condition when your body is not able to carry adequate oxygen to the tissues.
- The sickle cells die prematurely, resulting in a chronic lack of red blood cells.
- Furthermore, as they pass through small blood arteries, they become caught and obstruct the blood flow.
- This can result in discomfort as well as other dangerous consequences (health issues) such as infection, acute chest syndrome, and stroke.
- Babies with sickle cell anaemia may not exhibit symptoms for several months after birth.
- The symptoms of anaemia, however, include excessive weariness or fussiness, excruciatingly swollen hands and feet, and jaundice.
- Babies may also suffer spleen damage, which weakens their immune system and increases their susceptibility to bacterial infections.
- People with sickle cell anaemia may have various and increasingly significant medical problems as they age, which occur when organ tissues do not receive enough oxygen.
Diagnosing sickle cell disease-
- A blood test can determine whether you have SCD or sickle cell trait.
- People who are considering having children can get the test to determine the likelihood of their offspring having SCD.
- SCD can also be diagnosed before a baby is born. A sample of amniotic fluid (the fluids in the sac around the foetus) or placental tissue is used in this test (the organ that brings oxygen and nutrients to the baby).
Treatment therapies-
- SCD can only be cured by bone marrow or stem cell transplantation.
- These transplants are normally reserved for children with severe SCD since they are hazardous and can have substantial adverse effects.
- The bone marrow must be a close match for the transplant to succeed. A brother or sister is usually the ideal donor.
















