In news- Indian Vice President, M. Venkaiah Naidu, recently visited Senegal and three MoUs were signed by both sides. This was the first ever high level Indian visit to Senegal and took place at a time when both countries are celebrating 60 years of their diplomatic relations.
About Senegal-
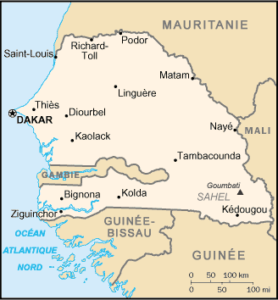
- Senegal is a country in West Africa, externally bounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the west, bordered by Mauritania in the north, Mali to the east, Guinea to the southeast, and Guinea-Bissau to the southwest.
- Senegal nearly surrounds the Gambia, a country occupying a narrow sliver of land along the banks of the Gambia River, which separates Senegal’s southern region of Casamance from the rest of the country.
- Senegal also shares a maritime border with Cape Verde.
- Senegal’s economic and political capital is Dakar.
- It is a unitary presidential republic and is the westernmost country in the mainland of the Old World, or Afro-Eurasia.
- It owes its name to the Senegal River, which borders it to the east and north.
- The state was formed as part of the independence of French West Africa from French colonial rule.
- The Wolof and French languages act as the country’s lingua francas.
- Senegal has a relatively low Human Development Index with most of the population being on the coast and works in agriculture or other food industries.
- It is a member state of the African Union, the United Nations, the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS), and the Community of Sahel-Saharan States.
- The Senegalese landscape consists mainly of the rolling sandy plains of the western Sahel which rise to foothills in the southeast.
- The northern border is formed by the Senegal River and other rivers include the Gambia and Casamance Rivers.
- India mainly imports phosphates, an important component of fertilizers, from Senegal.
















