In news– NASA will launch its first planetary defense test mission named the Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) on November 24, 2021.
About Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) mission
- DART is a planetary defense-driven test of technologies for preventing an impact of Earth by a hazardous asteroid.
- It will be the first demonstration of the kinetic impactor technique to change the motion of an asteroid in space.
- This mission is directed by NASA to the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) with support from several NASA centers.
- The target of the spacecraft is a small moonlet called Dimorphos (Greek for “two forms”).
- It is about 160-metre in diameter and the spacecraft is expected to collide when it is 11 million kilometres away from Earth.
- Dimorphos orbits a larger asteroid named Didymos (Greek for “twin”) which has a diameter of 780 metres.
- The mission is to test the new technology to be prepared in case an asteroid heads towards Earth in the future.
- The spacecraft will navigate to the moonlet and intentionally collide with it at a speed of about 6.6 kilometres per second or 24,000 kilometres per hour.
- The collision is expected to take place between September 26 and October 1, 2022.
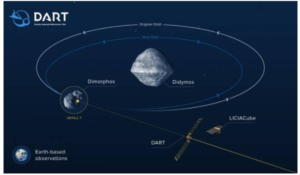
- It is believed that Didymos is a perfect system for the test mission because it is an eclipsing binary which means it has a moonlet that regularly orbits the asteroid and we can see it when it passes in front of the main asteroid.
- The timing for the DART impact is when the Didymos system is closest to the Earth.
About the spacecraft–
- It is a low-cost spacecraft, weighing around 610 kg at launch and 550 kg during impact.
- The main structure is a box (1.2 × 1.3 × 1.3 metres).
- It has two solar arrays and uses hydrazine propellant for maneuvering the spacecraft.
- It also carries about 10 kg of xenon which will be used to demonstrate the agency’s new thrusters called NASA Evolutionary Xenon Thruster–Commercial (NEXT-C) in space.
- NEXT has very high fuel efficiency and flexible operations making it ideal for many classes of science missions.
- The spacecraft carries a high-resolution imager called Didymos Reconnaissance and Asteroid Camera for Optical Navigation (DRACO).
- Images from DRACO will be sent to Earth in real-time and will help study the impact site and surface of Dimorphos.
- DART will also carry a small satellite or CubeSat named LICIACube (Light Italian CubeSat for Imaging of Asteroids).
- It will be deployed ten days before the impact on Dimorphos.
- LICIACube is expected to capture images of the impact and the impact crater formed as a result of the collision.
- Once launched, DART will deploy Roll Out Solar Arrays (ROSA) to provide the solar power needed for DART’s electric propulsion system.
















