About Blue Blob & slow melting of ice-
- The Blue Blob is a cold patch located south of Iceland and Greenland.
- The cold patch was most prominent during the winter of 2014-2015 when the sea surface temperature was about 1.4 degrees Celsius colder than normal.
- As per the recent study, starting in 2011, the speed of Iceland’s melting slowed, resulting in about half as much ice loss, or about five billion tons annually.
- The researchers found that cooler waters near the Blue Blob were linked to observations of lower air temperatures over Iceland’s glaciers and coincided with a slowing of glacial melting since 2011.
- Other scientists have proposed that the Blue Blob is part of the normal sea surface temperature variability in the Arctic.
- Before the Blue Blob, a long-term cooling trend in the same region, called the Atlantic Warming Hole, reduced sea surface temperatures by about 0.4 to 0.8 degrees Celsius during the last century and may continue to cool the region in the future.
- A possible explanation for the Warming Hole is that climate change has slowed the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), which is an ocean current that brings warm water up from the tropics to the Arctic, thus reducing the amount of heat delivered to the region.
The Arctic region-
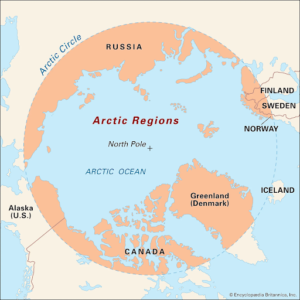
- The Arctic is a polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth.
- It is the area within the Arctic Circle, a line of latitude at 66.5° north of the Equator.
- Land within the Arctic region has seasonally varying snow and ice cover.
- It consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Alaska (United States), Canada, Finland, Greenland (Denmark), Iceland, Norway, Russia, and Sweden.
The Arctic Council
- It is the leading intergovernmental forum promoting cooperation, coordination and interaction among the Arctic States, Arctic indigenous communities and other Arctic inhabitants on common Arctic issues, in particular on issues of sustainable development and environmental protection in the Arctic.
- It was formally established in 1996.
- All Arctic Council decisions and statements require consensus of the eight Arctic States.
- Only states with territory in the Arctic can be members of the council.
- The member states consist of Canada, Denmark(representing Greenland), Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia, Sweden and the United States.
- The Ottawa Declaration defines these states as Members of the Arctic Council.
- The Council’s Strategic Plan 2021-2030 guides its work towards the Arctic as a “region of peace, stability and constructive cooperation, that is a vibrant, prosperous, sustainable and secure home for all its inhabitants, including Indigenous Peoples, and where their rights and wellbeing are respected.”
- Since 2013, India has had observer status in the Arctic Council.
Further reading: https://journalsofindia.com/indias-arctic-policy-2/
















