In News
Aajeevika – National Rural Livelihoods Mission (NRLM) was launched by the Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD), Government of India in June 2011. Aided in part through investment support by the World Bank, the Mission aims at creating efficient and effective institutional platforms of the rural poor, enabling them to increase household income through sustainable livelihood enhancements and improved access to financial services.
Features of NRLM
- NRLM set out with an agenda to cover 7 Crore rural poor households, across 600 districts, 6000 blocks, 2.5 lakh Gram Panchayats and 6 lakh villages in the country through self-managed Self Help Groups (SHGs) and federated institutions and support them for livelihoods collectives in a period of 8-10 years.
- In addition, the poor would be facilitated to achieve increased access to rights, entitlements and public services, diversified risk and better social indicators of empowerment.
- NRLM implementation is in a Mission Mode. This enables
. shift from the present allocation based strategy to a demand driven strategy enabling the states to formulate their own livelihoods-based poverty reduction action plans
. focus on targets, outcomes and time bound delivery
. continuous capacity building, imparting requisite skills and creating linkages with livelihoods opportunities for the poor, including those emerging in the organized sector
. monitoring against targets of poverty outcomes.
- As NRLM follows a demand driven strategy, the States have the flexibility to develop their livelihoods-based perspective plans and annual action plans for poverty reduction.
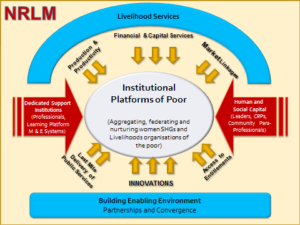
- NRLM rests on three major pillars – universal social mobilization, financial inclusion and livelihood enhancement. It works towards bringing at least one member (preferably a woman) from all poor families into the SHG network.
- The SHGs and their federations offer their members services such as savings, credit and livelihoods support. As the Institutions of the Poor (IoP) mature, they are facilitated to take up livelihoods/income-generating activities.
- The SRLMs are given the responsibility of implementing the programme in the states based on their States Perspective Implementation Plans (SPIPs) and Annual Action Plans (AAPs). District Mission Management Units (DMMU) and Block Mission Management Units (BMMU) are established to implement the programme.
- At the national level, the National Rural Livelihoods Promotion Society (NRLPS) has been set up to serve as the technical support agency to NRLM. NRLPS supports the SRLMs in strategizing, planning and implementing NRLM.
- The NRLM Target Households (NTH) are identified through the Participatory Identification of Poor (PIP) instead of the BPL. The PIP is a community-driven process where the community based organisations (CBOs) themselves identify the poor in the village using participatory tools. The list of poor identified by the CBO is vetted by the Gram Sabha.