How is the accreditation process carried out?
- NAAC relies heavily on self-assessment reports of applicant institutions.
- The first step has an applicant institution submitting a self-study report of information related to quantitative and qualitative metrics.
- The data is then validated by NAAC expert teams, followed by peer team visits to the institutions. This last step has sparked controversy.
Alternatives to current assesment approach-
- From the prevailing “input-based” approach, the NAAC plans to adopt an “outcome-based approach”.
- The white paper of NAAC states the current system is akin to accepting the claim of a PhD candidate that his thesis is of high quality.
- Instead, it suggests that emphasis should be on finding out if students are equipped with relevant skills and academic abilities.
- Rather than relying exclusively on the self-study reports of the HEIs, the NAAC should ask institutions to provide evidence such as samples of learning materials, continuous assessment tasks and final examinations to show they have outcomes of learning specified in the syllabus, according to the white paper.
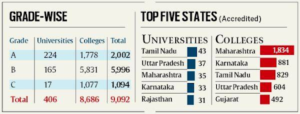
Accredited institutions in India-
- There are 1,043 universities and 42,343 colleges listed on the portal of the All India Survey on Higher Education.
- As per the latest data from June 21, there were 406 universities and 8,686 colleges that were NAAC-accredited.
- Among the states, Maharashtra accounts for the highest number of accredited colleges at 1,869 – more than twice as many as Karnataka’s 914, the second highest.
- Tamil Nadu has the most accredited universities at 43.
- Under the rules, only higher education institutions that are at least six years old, or from where at least two batches of students have graduated, can apply for accreditation.
- The accreditation is valid for five years. Aspiring institutes need to be recognised by the UGC and have regular students enrolled in their full-time teaching and research programmes.
- There are only 19 universities and 121 colleges that have been reviewed by the NAAC four times, with a gap of five years between each grading.
- When an institution undergoes the accreditation process for the first time it is referred to as Cycle 1, and the subsequent five-year periods as Cycles 2, 3 and so on.
- Earlier in 2022, NAAC explored the possibility of a new system of Provisional Accreditation for Colleges (PAC) under which even one-year-old institutions could apply for accreditation.
- The provisional certificates would be valid for two years. But the committee that drew up the white paper, which also underwent multiple rounds of revisions, observed that such a system can lead to compromise with quality.
About NAAC-
- The NAAC, an autonomous body under the University Grants Commission (UGC), assesses and certifies HEIs with gradings as part of accreditation.
- Through a multi-layered process, a higher education institution learns whether it meets the standards of quality set by the evaluator in terms of curriculum, faculty, infrastructure, research, and other parameters.
- The ratings of institutions range from A++ to C. If an institution is graded D, it means it is not accredited.
Further reading: https://journalsofindia.com/national-assessment-and-accreditation-council-naac/
















