In news– Recently, Israel has carried out strikes in the Gaza Strip after a rocket was fired from the Palestinian enclave into Israel.
About Gaza strip-
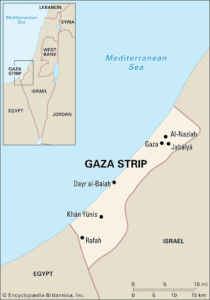
- The Gaza Strip is a Palestinian enclave situated on a relatively flat coastal plain on the eastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea.
- It borders Egypt on the southwest for 11 kilometres and Israel on the east and north along a 51 km border.
- The Gaza Strip and the West Bank are claimed by the de jure sovereign State of Palestine.
- The territories of Gaza and the West Bank are separated from each other by Israeli territory.
- Both fell under the jurisdiction of the Palestinian Authority, but the Strip has, since the Battle of Gaza in June 2007, been governed by Hamas, a militant, Palestinian, fundamentalist Islamic organization, which came to power in the last-held elections in 2006.
- It has been placed under an Israeli and US-led international economic and political boycott from that time onwards.
- The territory is 41 kilometres long, from 6 to 12 kilometres wide, and has a total area of 365 square kilometres.
History of the territory-
- After rule by the Ottoman Empire ended there in World War I (1914–18), the Gaza area became part of the League of Nations mandate of Palestine under British rule.
- Before this mandate ended, the General Assembly of the United Nations (UN) in November 1947 accepted a plan for the Arab-Jewish partition of Palestine under which the town of Gaza and an area of surrounding territory were to be allotted to the Arabs.
- The British mandate ended on May 15, 1948, and on that same day the first Arab-Israeli war began.
- Egyptian forces soon entered the town of Gaza, which became the headquarters of the Egyptian expeditionary force in Palestine.
- As a result of heavy fighting in autumn 1948, the area around the town under Arab occupation was reduced to a strip of territory 25 miles (40 km) long and 4–5 miles (6–8 km) wide.
- This area became known as the Gaza Strip and its boundaries were demarcated in the Egyptian-Israeli armistice agreement of February 24, 1949.
- It was under Egyptian military rule from 1949 to 1956 and again from 1957 to 1967.
- In the Six-Day War of June 1967, the Gaza Strip was again taken by Israel, which occupied the region for the next quarter century.
- In December 1987 rioting and violent street clashes between Gaza’s Palestinians and occupying Israeli troops marked the birth of an uprising that came to be known as the intifada ( “shaking off”).
- In 1994, Israel began a phased transfer of governmental authority in the Gaza Strip to the Palestinian Authority (PA) under the terms of the Oslo Accords that were signed by Israel and the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO).
- Beginning in late 2000, a breakdown in negotiations between the PA and Israel was followed by a further, more extreme outbreak of violence, termed the second, or Aqṣā, intifada.
- In an effort to end the fighting, Israeli Prime Minister Ariel Sharon announced in late 2003 a plan that centred on withdrawing Israeli soldiers and settlers from the Gaza Strip.
- In September 2005 Israel completed the pullout from the territory, and control of the Gaza Strip was transferred to the PA, although Israel continued to patrol its borders and airspace.
















