In news–Due to violent protests, Kazakhstan has sought assistance from the Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO) recently.
About Kazakhstan-
- It is a Central Asian country and former Soviet republic, declared independent on December 16, 1991.
- It is bounded on the northwest and north by Russia, on the east by China, and on the south by Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan, the Aral Sea, and Turkmenistan; the Caspian Sea bounds Kazakhstan to the southwest.
- Its capital is Nur-Sultan (formerly known as Astana) and its currency is Kazakhstani tenge.
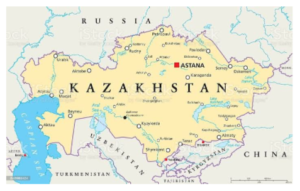
- Kazakhstan is the largest country in Central Asia and the ninth largest in the world.
- The local ethnos – Kazakhs make the largest part of the population – 58.9%, followed by Russian, Ukrainians, Uzbeks, Uighur, Tatar and German.
- Lowlands make up one-third of Kazakhstan’s huge expanse, followed by hilly plateaus and plains.
- Kazakhstan’s highest point, Mount Khan-Tengri at 22,949 feet (6,995 metres), in the Tien Shan range on the border between Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and China, contrasts with the flat or rolling terrain of most of the republic.
- The western and southwestern parts of the republic are dominated by the low-lying Caspian Depression, which at its lowest point lies some 95 feet below sea level.
- South of the Caspian Depression are the Ustyurt Plateau and the Tupqaraghan (formerly Mangyshlak) Peninsula jutting into the Caspian Sea.
- Vast amounts of sand form the Greater Barsuki and Aral Karakum deserts near the Aral Sea, the broad Betpaqdala Desert of the interior, and the Muyunkum and Kyzylkum deserts in the south.
- Depressions filled by salt lakes whose water has largely evaporated dot the undulating uplands of central Kazakhstan.
- Kazakhstan’s climate is sharply continental, and hot summers alternate with equally extreme winters, especially in the plains and valleys.
Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO)-
- It is an intergovernmental military alliance in Eurasia, founded in 1992.
- It consists of select post-Soviet states as members namely Russia, Armenia, Belarus, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and Kazakhstan.
- Its purpose is to ensure the collective defence of any member that faces external aggression.
- It has been described by political scientists as the Eurasian counterpart of NATO.
- It supports arms sales and manufacturing as well as military training and exercises.
- Afghanistan and Serbia hold observer status in the CSTO.
- The organization uses a rotating presidency system in which the state leading the CSTO changes every year.
- Beyond mutual defence, the CSTO also coordinates efforts in fighting the illegal circulation of weapons among member states and has developed law enforcement training for its members in pursuit of these aims.
- Members also use the organization to counter cyber warfare, narcotics trafficking, the illegal circulation of weapons, transnational crime, and terrorism.
- There are two regional groups (Russia-Belarus and Russia-Armenia).
- While CSTO membership means that member states are barred from joining other military alliances, limiting, for example, their relationship with NATO, members receive discounts, subsidies, and other incentives to buy Russian arms, facilitating military cooperation.
















