About Good Governance Index (GGI)-
- It is a uniform tool across States to assess the Status of Governance and impact of various interventions taken up by the State Government and UTs.
- Though the states and UTs are ranked on all indicators separately, composite ranking is also calculated for these states and UTs under their respective groups based upon these indicators.
Objectives of GGI:
- To provide quantifiable data to compare the state of governance in all states and UTs.
- Enabling the states and UTs to formulate and implement suitable strategies for improving governance.
- Encouraging states to shift to result oriented approaches and administration.
- GGI 2021 Framework covered ten sectors and 58 indicators.
- The sectors of GGI 2020-21 are Agriculture and Allied Sectors, Commerce & Industries, Human Resource Development, Public Health, Public Infrastructure & Utilities, Economic Governance, Social Welfare & Development, Judicial & Public Security, Environment, and Citizen-Centric Governance.
- The GGI 2020-21 categorizes States and UTs into four categories, i.e., (i) Other States – Group A; (ii) Other States – Group B; (iii) North-East and Hill States; and (iv) Union Territories.
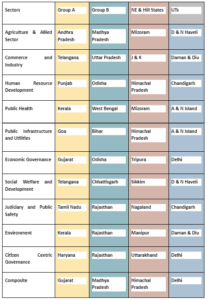
- Gujarat, Maharashtra and Goa top the composite rank score covering 10 sectors.
Top ranking States in the Sectors as well as in Composite Ranks is as follows:
Good governance:
- Governance is the process of decision-making and the process by which decisions are implemented (or not implemented).
- Government is one of the actors in governance.
- Other actors involved in governance vary from landlords, associations of peasant farmers, cooperatives, NGOs, research institutes, religious leaders to media, lobbyists, international donors, multinational corporations, etc.
- All the related actors play a major role in decision- making or in influencing the decision-making process.
- Good governance assures that corruption is minimized, the views of minorities are taken into account and that the voices of the most vulnerable in society are heard in decision-making

It has 8 major characteristics:
- Participation: Participation by both men and women is a key cornerstone of good governance. Participation could be either direct or through legitimate intermediate institutions or representatives.
- Rule of law: Good governance requires fair legal frameworks that are enforced impartially.
- Transparency: The decisions taken and their enforcement are done in a manner that follows rules and regulations. It also means that information is freely available and directly accessible to those who will be affected by such decisions and their enforcement.
- Responsiveness: Good governance requires that institutions and processes try to serve all stakeholders within a reasonable time frame.
- Consensus oriented: Good governance requires mediation of the different interests in society to reach a broad consensus which is in the best interest of the whole community.
- Equity and inclusiveness: A society’s well being depends on ensuring that all its members (especially vulnerable) feel that they have a stake in it and do not feel excluded from the mainstream of society.
- Effectiveness and efficiency: The processes and institutions produce results that meet the needs of society while making the sustainable use of resources at their disposal.
- Accountability: The governmental institutions, private sector and civil society organizations must be accountable to the public and to their institutional stakeholders.
















