In news-Recently, eight of India’s major banks have joined the Account Aggregator (AA) network that will enable customers to easily access and share their financial data.
What is an Account Aggregator (AA)?
- It is a non-banking financial company engaged in the business of providing, under a contract, the service of retrieving or collecting financial information pertaining to its customer.
- It is also engaged in consolidating, organising and presenting such information to the customer or any other financial information user as may be specified by the bank.
Which banks have joined it?
Eight of India’s major banks State Bank of India, ICICI Bank, Axis Bank, IDFC First Bank, Kotak Mahindra Bank, HDFC Bank, IndusInd Bank and Federal Bank have joined the Account Aggregator (AA) network.
Account Aggregator framework
- The AA framework was created through an inter-regulatory decision by RBI and other regulators including SEBI, IRDA, and PFRDA through an initiative of the Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC).
- The licence for AAs is issued by the RBI, and the financial sector will have many AAs.
- The AA framework allows customers to avail various financial services from a host of providers on a single portal based on a consent method, under which the consumers can choose what financial data to share and with which entity.
- The framework, which has been under discussion since 2016 and in the testing phase for some time, will now be open to all customers.
Role of an Account Aggregator
- An AA reduces the need for individuals to wait in long bank queues, use Internet banking portals, share their passwords, or seek out physical notarisation to access and share their financial documents.
- It will allow banks to access consented data flows and verified data.
- This will help banks reduce transaction costs, which will enable banks to offer lower ticket size loans and more tailored products and services to our customers.
- It will also help banks reduce frauds and comply with upcoming privacy laws.
How does it work?
- It has a three-tier structure — Account Aggregator, Financial Information Provider(FIP) and Financial Information User(FIU).
- An FIP is the data fiduciary, which holds customers’ data. It can be a bank, NBFC, mutual fund, insurance repository or pension fund repository.
- An FIU consumes the data from an FIP to provide various services to the consumer.
- An FIU is a lending bank that wants access to the borrower’s data to determine if the borrower qualifies for a loan. Banks play a dual role – as an FIP and as an FIU.
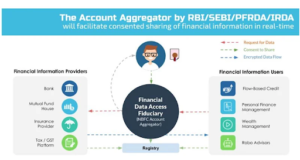
- An AA should not support transactions by customers but should ensure appropriate mechanisms for proper customer identification.
- An AA should share information only with the customer to whom it relates or any other financial information user as authorised by the customer.
















